1. What is DuPont Analysis Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes ROE and its components (NPM, TAT, FL) using the DuPont formula.
Purpose: Helps analyze a company’s profitability, efficiency, and leverage to assess shareholder value creation.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses these formulas:
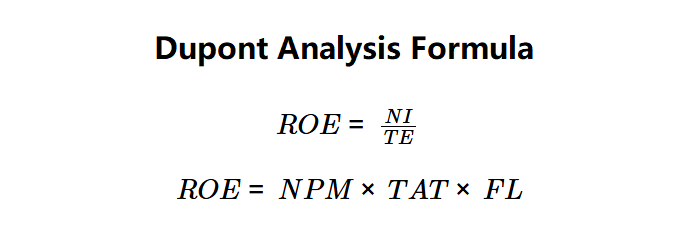
ROE:
\( ROE = \frac{NI}{TE} \)
or
\( ROE = NPM \times TAT \times FL \)
Where:
- \( NI \): Net Income (dollars)
- \( TE \): Total Equity (dollars)
NPM:
\( NPM = \frac{NI}{R} \)
or
\( NPM = \frac{ROE}{TAT \times FL} \)
Where:
- \( R \): Revenue (dollars)
TAT:
\( TAT = \frac{R}{TA} \)
or
\( TAT = \frac{ROE}{NPM \times FL} \)
Where:
- \( TA \): Total Assets (dollars)
FL:
\( FL = \frac{TA}{TE} \)
or
\( FL = \frac{ROE}{NPM \times TAT} \)
Steps:
- Enter net income, revenue, total assets, and total equity.
- Calculate ROE, NPM, TAT, and FL.
- Display results with 2 decimal places.
3. Importance of DuPont Analysis
Calculating DuPont components is crucial for:
- Profitability: Assesses how efficiently revenue turns into profit (NPM).
- Efficiency: Evaluates asset use effectiveness (TAT).
- Leverage: Measures risk from debt financing (FL).
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1: NI = $100,000, R = $500,000, TA = $1,000,000, TE = $400,000:
- \( NPM = \frac{100,000}{500,000} = 20.00\% \)
- \( TAT = \frac{500,000}{1,000,000} = 0.50 \)
- \( FL = \frac{1,000,000}{400,000} = 2.50 \)
- \( ROE = 20.00 \times 0.50 \times 2.50 = 25.00\% \)
- Result: ROE = 25.00%, NPM = 20.00%, TAT = 0.50, FL = 2.50
Example 2: NI = $50,000, R = $200,000, TA = $800,000, TE = $300,000:
- \( NPM = \frac{50,000}{200,000} = 25.00\% \)
- \( TAT = \frac{200,000}{800,000} = 0.25 \)
- \( FL = \frac{800,000}{300,000} = 2.67 \)
- \( ROE = 25.00 \times 0.25 \times 2.67 = 16.68\% \)
- Result: ROE = 16.68%, NPM = 25.00%, TAT = 0.25, FL = 2.67
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does a high ROE indicate?
A: A high ROE may reflect strong profitability, efficiency, or leverage, but excessive leverage could signal risk.
Q: Why use DuPont analysis?
A: It breaks down ROE to identify specific areas (NPM, TAT, FL) driving performance or risks.
Q: Can FL be too high?
A: Yes, a high FL indicates heavy debt, increasing bankruptcy risk if not managed properly.
DuPont Analysis Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back