 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: The Debt-to-Income (DTI) Ratio Calculator measures the percentage of your gross monthly income that goes toward paying monthly debt obligations, including housing and non-housing debts. It calculates both front-end (housing-related) and back-end (total debt) DTI ratios.
Purpose: This tool helps users assess their financial health and loan eligibility, as lenders use DTI to determine your ability to manage additional debt payments, especially for mortgages or other loans.
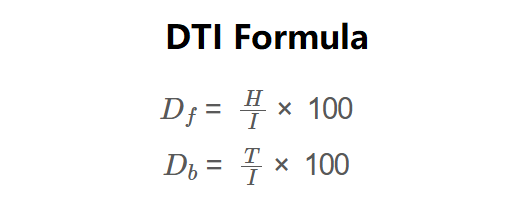
The calculator uses the following formulas:
\( D_f = \frac{H}{I} \times 100 \)
\( D_b = \frac{T}{I} \times 100 \)
Where:
Steps:
Calculating your DTI ratio is essential for:
Example: Calculate the DTI for a person with $5,000 gross monthly income, $1,000 mortgage payment, $300 car loan, and $200 credit card payment:
A back-end DTI of 30% is healthy, indicating good financial management and likely mortgage eligibility.
Q: What is a good DTI ratio?
A: A back-end DTI below 36% is ideal, with 20% or lower considered excellent. For mortgages, a front-end DTI below 28% is preferred.
Q: What debts are included in DTI?
A: Include recurring monthly payments like mortgage/rent, car loans, student loans, credit card minimums, and child support. Exclude utilities, groceries, or other non-debt expenses.
Q: How can I lower my DTI?
A: Pay down debts, avoid new loans, or increase income through side jobs or salary increases. Budgeting to cut unnecessary expenses can also help.