 Home
Home
 Back
Back
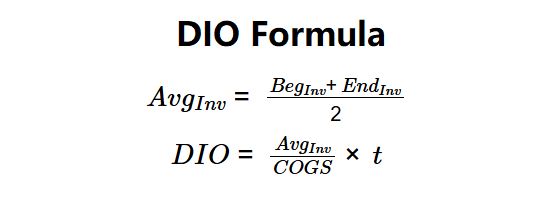
Definition: This calculator computes the days inventory outstanding (\( DIO \)), which measures the average number of days it takes a company to sell its entire inventory, indicating inventory management efficiency.
Purpose: Helps businesses and analysts evaluate inventory turnover, optimize stock levels, and improve cash flow management.
The calculator uses a two-step process to compute DIO:
Formulas:
Steps:
Calculating DIO is crucial for:
Example 1 (Company Alpha): \( Beg_{Inv} = \$500,000 \), \( End_{Inv} = \$750,000 \), \( COGS = \$6,500,000 \), \( t = 365 \):
A DIO of 35.10 days indicates efficient inventory turnover.
Example 2: \( Beg_{Inv} = \$200,000 \), \( End_{Inv} = \$300,000 \), \( COGS = \$2,000,000 \), \( t = 365 \):
A DIO of 45.63 days suggests slower inventory turnover, potentially tying up capital.
Example 3: \( Beg_{Inv} = \$1,000,000 \), \( End_{Inv} = \$1,200,000 \), \( COGS = \$10,000,000 \), \( t = 365 \):
A DIO of 40.15 days indicates moderate inventory turnover efficiency.
Q: What is days inventory outstanding?
A: Days inventory outstanding (\( DIO \)) is the average number of days it takes to sell the entire inventory, reflecting inventory management efficiency.
Q: What is a good DIO value?
A: A lower \( DIO \) (e.g., 30-60 days) is generally better, indicating faster inventory turnover, though this varies by industry.
Q: Can DIO be negative?
A: No, since \( Avg_{Inv} \), \( COGS \), and \( t \) are non-negative, \( DIO \) is non-negative.