 Home
Home
 Back
Back
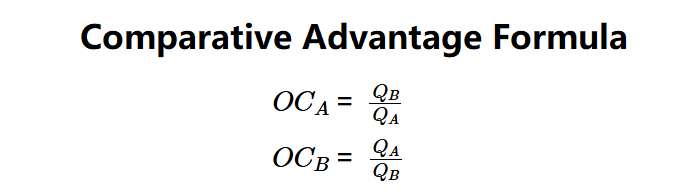
Definition: The Comparative Advantage Calculator computes the opportunity costs of producing two goods in two countries to determine which country has a comparative advantage in each good, based on lower opportunity costs. It uses outputs per unit of labor to analyze trade efficiency.
Purpose: Helps businesses, economists, and policymakers identify which goods countries should specialize in to maximize trade benefits and economic efficiency.
The calculator computes opportunity costs to identify comparative advantages, following these steps and formulas:
Formulas:
Comparative advantage is assigned to the country with the lower opportunity cost for each good.
Steps:
Calculating comparative advantage is crucial for:
Example (Country X and Country Y): Country X: \( Q_A = 110 \), \( Q_B = 100 \); Country Y: \( Q_A = 80 \), \( Q_B = 90 \):
Country X should specialize in Good B and Country Y in Good A to maximize trade efficiency.
Q: What is comparative advantage?
A: It’s the ability of a country to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another country, guiding specialization and trade.
Q: How does it differ from absolute advantage?
A: Absolute advantage is producing more of a good with the same resources; comparative advantage is producing with lower opportunity cost, even if less efficient overall.
Q: Why is comparative advantage important?
A: It promotes efficient resource use and global trade benefits by encouraging specialization in goods with the lowest opportunity costs.