 Home
Home
 Back
Back
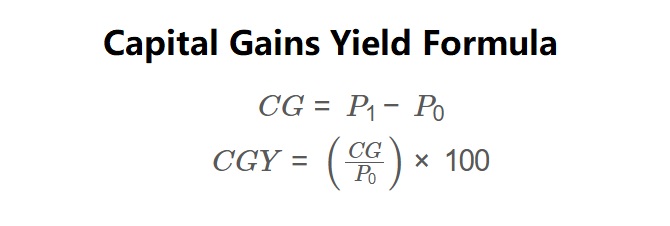
Definition: This calculator computes the Capital Gains (\( CG \)) and Capital Gains Yield (\( CGY \)) of an investment based on its Bought Price (\( P_0 \)) and Current Price (\( P_1 \)). \( CGY \) represents the percentage increase (or decrease) in the price of an investment, excluding dividends.
Purpose: Investors use this tool to evaluate the price appreciation of investments like stocks or bonds, helping to assess performance and inform decisions about buying, holding, or selling.
The calculator uses the following formulas, as shown in the image above:
\( CG = P_1 - P_0 \)
\( CGY = \left( \frac{CG}{P_0} \right) \times 100 \)
Where:
Steps:
Calculating Capital Gains Yield is essential for:
Example 1: Calculate the Capital Gains and Capital Gains Yield for a stock bought at $100 and now worth $120, in USD:
Example 2: Calculate the Capital Gains and Capital Gains Yield for a stock bought at €50 and now worth €40, in EUR:
Q: Why doesn’t the Capital Gains Yield include dividends?
A: \( CGY \) focuses solely on price appreciation to isolate the growth component of an investment’s return. Dividends are accounted for in the total return or dividend yield.
Q: Can Capital Gains Yield be negative?
A: Yes, if the Current Price is less than the Bought Price, the \( CGY \) will be negative, indicating a capital loss.
Q: How does Capital Gains Yield help with tax planning?
A: Understanding \( CG \) and \( CGY \) helps estimate potential taxable gains, allowing investors to plan for tax liabilities.