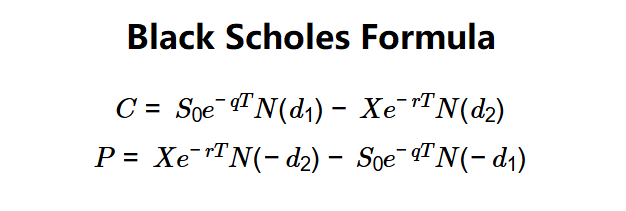1. What is the Black-Scholes Option Pricing Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the theoretical prices of European call and put options using the Black-Scholes model, a mathematical framework for pricing options contracts.
Purpose: Assists traders, investors, and financial analysts in estimating option prices based on market parameters, aiding in investment decisions and risk management.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the Black-Scholes formulas to compute option prices:
Formulas:
\( C = S_0 e^{-qT} N(d_1) - X e^{-rT} N(d_2) \)
\( P = X e^{-rT} N(-d_2) - S_0 e^{-qT} N(-d_1) \)
Where:
- \( d_1 = \frac{\ln\left(\frac{S_0}{X}\right) + \left(r - q + \frac{v^2}{2}\right)T}{v \sqrt{T}} \)
- \( d_2 = \frac{\ln\left(\frac{S_0}{X}\right) + \left(r - q - \frac{v^2}{2}\right)T}{v \sqrt{T}} \)
- \( C \): Call option price (dollars)
- \( P \): Put option price (dollars)
- \( S_0 \): Current stock price (dollars)
- \( X \): Strike price (dollars)
- \( T \): Time to expiration (years)
- \( r \): Risk-free interest rate (decimal)
- \( q \): Dividend yield (decimal)
- \( v \): Annualized volatility (decimal)
- \( N(\cdot) \): Cumulative standard normal distribution function
Steps:
- Step 1: Input parameters. Enter the current stock price (\( S_0 \)), strike price (\( X \)), time to expiration (\( T \)), risk-free rate (\( r \)), dividend yield (\( q \)), and volatility (\( v \)).
- Step 2: Calculate \( d_1 \) and \( d_2 \). Compute the intermediate variables using the provided formulas.
- Step 3: Compute option prices. Calculate the call (\( C \)) and put (\( P \)) prices using the Black-Scholes formulas.
3. Importance of Black-Scholes Calculation
Calculating option prices with the Black-Scholes model is crucial for:
- Pricing Accuracy: Provides a standardized method to estimate fair option prices, widely used in financial markets Investopedia.
- Risk Management: Helps traders assess option sensitivity to market changes (e.g., via Greeks like Delta and Vega).
- Investment Decisions: Enables investors to compare theoretical prices with market prices to identify mispriced options.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1: \( S_0 = \$100 \), \( X = \$100 \), \( T = 1 \), \( r = 5\% \), \( q = 2\% \), \( v = 20\% \):
- Step 1: Input \( S_0 = 100 \), \( X = 100 \), \( T = 1 \), \( r = 5 \), \( q = 2 \), \( v = 20 \).
- Step 2: Calculate \( d_1 = \frac{\ln(100/100) + (0.05 - 0.02 + (0.2^2/2)) \cdot 1}{0.2 \sqrt{1}} \approx 0.225 \), \( d_2 = 0.225 - 0.2 \sqrt{1} \approx 0.025 \).
- Step 3: Compute \( C \approx 100 \cdot e^{-0.02 \cdot 1} \cdot N(0.225) - 100 \cdot e^{-0.05 \cdot 1} \cdot N(0.025) \approx 10.45 \), \( P \approx 100 \cdot e^{-0.05 \cdot 1} \cdot N(-0.025) - 100 \cdot e^{-0.02 \cdot 1} \cdot N(-0.225) \approx 5.57 \).
- Results: \( C \approx \$10.45 \), \( P \approx \$5.57 \).
These prices suggest the call and put options are fairly valued for the given parameters.
Example 2: \( S_0 = \$50 \), \( X = \$55 \), \( T = 0.5 \), \( r = 3\% \), \( q = 0\% \), \( v = 30\% \):
- Step 1: Input \( S_0 = 50 \), \( X = 55 \), \( T = 0.5 \), \( r = 3 \), \( q = 0 \), \( v = 30 \).
- Step 2: Calculate \( d_1 = \frac{\ln(50/55) + (0.03 - 0 + (0.3^2/2)) \cdot 0.5}{0.3 \sqrt{0.5}} \approx -0.222 \), \( d_2 = -0.222 - 0.3 \sqrt{0.5} \approx -0.434 \).
- Step 3: Compute \( C \approx 50 \cdot e^{0 \cdot 0.5} \cdot N(-0.222) - 55 \cdot e^{-0.03 \cdot 0.5} \cdot N(-0.434) \approx 3.15 \), \( P \approx 55 \cdot e^{-0.03 \cdot 0.5} \cdot N(0.434) - 50 \cdot e^{0 \cdot 0.5} \cdot N(0.222) \approx 7.28 \).
- Results: \( C \approx \$3.15 \), \( P \approx \$7.28 \).
The put option is more expensive due to the stock being below the strike price.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a good option price?
A: The Black-Scholes model provides theoretical prices; compare these to market prices to assess if an option is over- or underpriced.
Q: Can the model handle American options?
A: No, the Black-Scholes model is designed for European options. American options require other methods like binomial models.
Q: How is volatility determined?
A: Volatility is typically estimated from historical stock price data or implied from current option market prices.
Black-Scholes Option Pricing Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back