 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Note: This is an estimate based on general assumptions. For a precise calculation, consult an HVAC professional to perform a Manual J load calculation, which considers factors like climate, insulation, and windows.
Definition: This calculator estimates the cooling capacity (tonnage) required for an HVAC system based on the area to be cooled, number of occupants, windows, and exterior doors.
Purpose: It helps homeowners estimate the HVAC system size needed to cool their space, ensuring comfort and energy efficiency.
The calculator uses the following method:
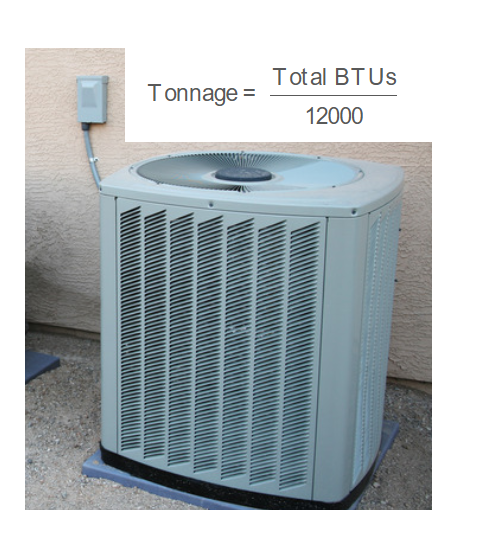
Formulas: \[ \text{Base BTUs} = \text{Area (sq ft)} \times 25 \] \[ \text{People BTUs} = \text{Number of People} \times 400 \] \[ \text{Windows BTUs} = \text{Number of Windows} \times 1000 \] \[ \text{Doors BTUs} = \text{Number of Exterior Doors} \times 1000 \] \[ \text{Total BTUs} = \text{Base BTUs} + \text{People BTUs} + \text{Windows BTUs} + \text{Doors BTUs} \] \[ \text{Tonnage} = \frac{\text{Total BTUs}}{12000} \] Where:
Unit Conversions:
Steps:
Estimating the correct tonnage is crucial for:
Examples:
Q: What does HVAC tonnage mean?
A: HVAC tonnage refers to the cooling capacity of an air conditioner, where 1 ton equals 12,000 BTUs per hour—the amount of heat needed to melt 1 ton of ice in 24 hours.
Q: Why include occupants, windows, and doors in the calculation?
A: Occupants add heat through body warmth, while windows and doors increase heat gain due to potential air leakage and solar radiation.
Q: Is this calculator’s estimate sufficient for purchasing an HVAC system?
A: No, this is an estimate. A professional Manual J load calculation is recommended to account for factors like insulation, climate, and windows for precise sizing.