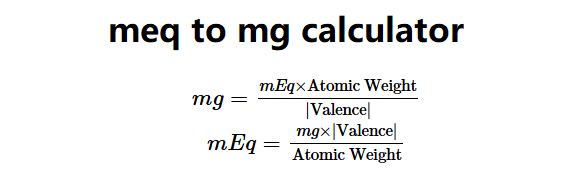mEq to mg and mg to mEq Calculator
How to Calculate Between mEq and mg
The mEq to mg and mg to mEq Calculator converts between milliequivalents (mEq) and milligrams (mg) for ions or molecules in water solutions. The formulas are:
\( mg = \frac{mEq \times \text{Atomic Weight}}{|\text{Valence}|} \)
\( mEq = \frac{mg \times |\text{Valence}|}{\text{Atomic Weight}} \)
Where:
- \( mg \): Milligrams, a unit of mass.
- \( mEq \): Milliequivalents, a unit of chemical activity based on ion charge.
- \( \text{Atomic Weight} \): Atomic or molecular weight in g/mol (e.g., 39.1 for K⁺, 40.08 for Ca²⁺).
- \( \text{Valence} \): Absolute ion charge (e.g., 1 for K⁺, 2 for Ca²⁺).
Select the conversion direction, enter the input value, atomic/molecular weight, and ion valence, then calculate the result.
Note: The conversion requires the atomic or molecular weight and valence of the ion or molecule, typically found in periodic tables or chemical references.
Using the mEq and mg Mutual Conversion Calculator
This calculator is useful for chemistry, medical, and water quality applications, converting between mEq and mg for electrolytes like potassium, calcium, etc.
Select the direction (mEq to mg or mg to mEq), input the value, atomic/molecular weight, and ion valence. The calculator outputs the converted value.
Example 1: For 100 mEq of potassium (K⁺) to mg.
- Direction: mEq to mg
- Input: \( 100 \, \text{mEq} \)
- Atomic Weight: \( 39.1 \, \text{g/mol} \) (for K⁺)
- Valence: \( 1 \)
- Calculation: \( mg = \frac{100 \times 39.1}{1} = 3910 \)
- Result: \( 3910 \, \text{mg} \)
Example 2: For 200 mg of calcium (Ca²⁺) to mEq.
- Direction: mg to mEq
- Input: \( 200 \, \text{mg} \)
- Atomic Weight: \( 40.08 \, \text{g/mol} \) (for Ca²⁺)
- Valence: \( 2 \)
- Calculation: \( mEq = \frac{200 \times 2}{40.08} = 9.98 \)
- Result: \( 9.98 \, \text{mEq} \)
Use this tool for precise conversions in chemical or medical analysis.
Common FAQ
Below are frequently asked questions about mEq and mg conversions:
- Q: What is mEq?
A: mEq stands for milliequivalents, a measure of chemical activity based on ion charge.
- Q: What is mg?
A: mg stands for milligrams, a unit of mass.
- Q: Why do I need atomic weight and valence?
A: These are required to account for the ion's chemical properties in the conversion.
- Q: How accurate is this calculator?
A: It provides precise results based on the formulas, rounded to 3 decimal places.
- Q: Can negative values be used?
A: No, input values, atomic weight, and valence must be positive; invalid inputs leave the result blank.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back