1. What is the Watts to Volts Calculator?
Definition: This calculator converts power in watts to voltage in volts for DC and AC circuits, using either current in amps or resistance in ohms. It supports DC, AC single-phase, and AC three-phase circuits.
Purpose: It is used in electrical engineering to determine voltage based on power consumption, aiding in circuit design and troubleshooting.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
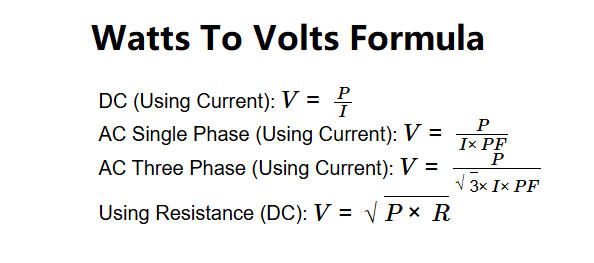
Formulas:
- DC (Using Current): \( V = \frac{P}{I} \)
- AC Single Phase (Using Current): \( V = \frac{P}{I \times PF} \)
- AC Three Phase (Using Current): \( V = \frac{P}{\sqrt{3} \times I \times PF} \)
- Using Resistance (DC): \( V = \sqrt{P \times R} \)
where:
- \( P \): Power in watts (W)
- \( I \): Current in amps (A)
- \( PF \): Power factor (unitless, 0-1)
- \( R \): Resistance in ohms (\(\Omega\))
- \( V \): Voltage in volts (V)
Steps:
- Select the calculation mode: Using Current or Using Resistance.
- If Using Current, select circuit type: DC, AC Single Phase, or AC Three Phase.
- Enter power in watts (default 20, step 0.01).
- If Using Current, enter current in amps (default 4).
- If AC, enter power factor (default 0.9).
- If Using Resistance, enter resistance in ohms (default 10).
- Calculate the voltage, rounded to 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Watts to Volts Conversion
Calculating watts to volts is crucial for:
- Electrical Design: Ensures proper voltage levels for devices and circuits.
- Power Systems: Helps in sizing components for DC and AC systems.
- Troubleshooting: Identifies issues in power delivery.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1 (DC Using Current): 20 W, 4 A:
- Voltage: \( 20 / 4 = 5 \) V
- Result: Voltage = 5.0000 V
- Example 2 (AC Single Phase): 1300 W, 12 A, PF 0.9:
- Voltage: \( 1300 / (12 \times 0.9) = 120.3704 \) V (rounded)
- Result: Voltage = 120.3704 V
- Example 3 (AC Three Phase): 1300 W, 12 A, PF 0.9:
- Voltage: \( 1300 / (\sqrt{3} \times 12 \times 0.9) \approx 69.4444 \) V
- Result: Voltage = 69.4444 V
- Example 4 (Using Resistance): 40 W, 10 \(\Omega\):
- Voltage: \( \sqrt{40 \times 10} = 20 \) V
- Result: Voltage = 20.0000 V
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is Watt’s Law?
A: Watt’s Law states that power (P) is equal to voltage (V) times current (I), or P = V × I.
Q: Why include power factor for AC?
A: Power factor accounts for the phase difference between voltage and current in AC circuits.
Q: What are common applications?
A: Used in power supplies, electrical installations, and renewable energy systems like solar panels.
Watts to Volts Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back