 Home
Home
 Back
Back
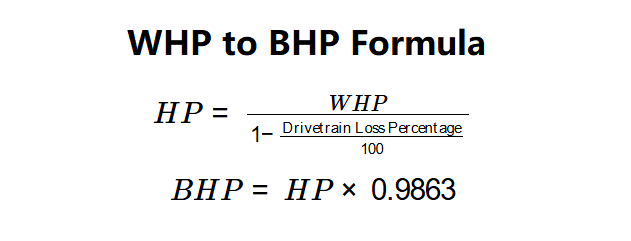
Definition: This calculator converts wheel horsepower (WHP) to brake horsepower (BHP) by accounting for drivetrain power losses, using the formulas \( HP = \frac{WHP}{1 - \text{Drivetrain Loss Percentage}} \) and \( BHP = HP \times 0.9863 \).
Purpose: It assists automotive enthusiasts, engineers, and mechanics in estimating the engine’s brake horsepower based on wheel horsepower measurements, useful for vehicle performance analysis.
The calculator uses the equations:
Where:
Steps:
Calculating BHP from WHP is crucial for:
Example 1: Calculate the BHP for a car with \( WHP = 200 \) and \( \text{Drivetrain Loss} = 15\% \), result in BHP:
Example 2: Calculate the HP for a car with \( WHP = 150 \) and \( \text{Drivetrain Loss} = 20\% \), result in HP:
Q: What is wheel horsepower (WHP)?
A: Wheel horsepower is the power measured at the wheels of a vehicle, accounting for drivetrain losses.
Q: What is brake horsepower (BHP)?
A: Brake horsepower is the power output of an engine before drivetrain losses, measured at the crankshaft.
Q: Why must WHP be non-negative?
A: WHP represents power output, which cannot be negative in realistic scenarios.
Q: Why is drivetrain loss limited to 0–99.9%?
A: Drivetrain loss must be less than 100% to avoid division by zero and ensure physically meaningful results.
Q: How accurate is the drivetrain loss formula?
A: The formula assumes a constant loss percentage, which is an approximation; actual losses vary by vehicle and conditions.
Q: What is a typical drivetrain loss percentage?
A: Typical drivetrain losses range from 10–20% for front-wheel drive, 15–25% for rear-wheel drive, and 20–30% for all-wheel drive vehicles.
Q: Why is there a conversion factor of 0.9863?
A: The factor 0.9863 accounts for the slight difference between horsepower definitions, aligning BHP with standard HP measurements.
Q: Can this calculator be used for motorcycles?
A: Yes, it applies to any vehicle with measured WHP and known drivetrain loss, including motorcycles.
Q: Why are results sometimes in scientific notation?
A: Results less than 0.001 are shown in scientific notation for readability, per the calculator’s formatting.
Q: How do I estimate drivetrain loss?
A: Drivetrain loss can be estimated based on vehicle type or measured using dynamometer tests comparing engine and wheel power.
Q: Is this calculator useful for performance tuning?
A: Yes, it helps estimate engine power from dyno-measured WHP, aiding in tuning and modification planning.
Q: Can this be used for electric vehicles?
A: Yes, if WHP and drivetrain loss are known, though electric vehicles often use kW instead of HP.
Q: Does this account for other power losses?
A: No, it only accounts for drivetrain loss; other losses (e.g., parasitic losses) require separate calculations.
Q: How can I verify the calculated BHP?
A: Use a dynamometer to measure engine output directly, as this calculator relies on estimated drivetrain loss.
Q: What if I don’t know the drivetrain loss?
A: Use an average loss percentage (e.g., 15–20%) for your vehicle type, but note that results will be approximate.