 Home
Home
 Back
Back
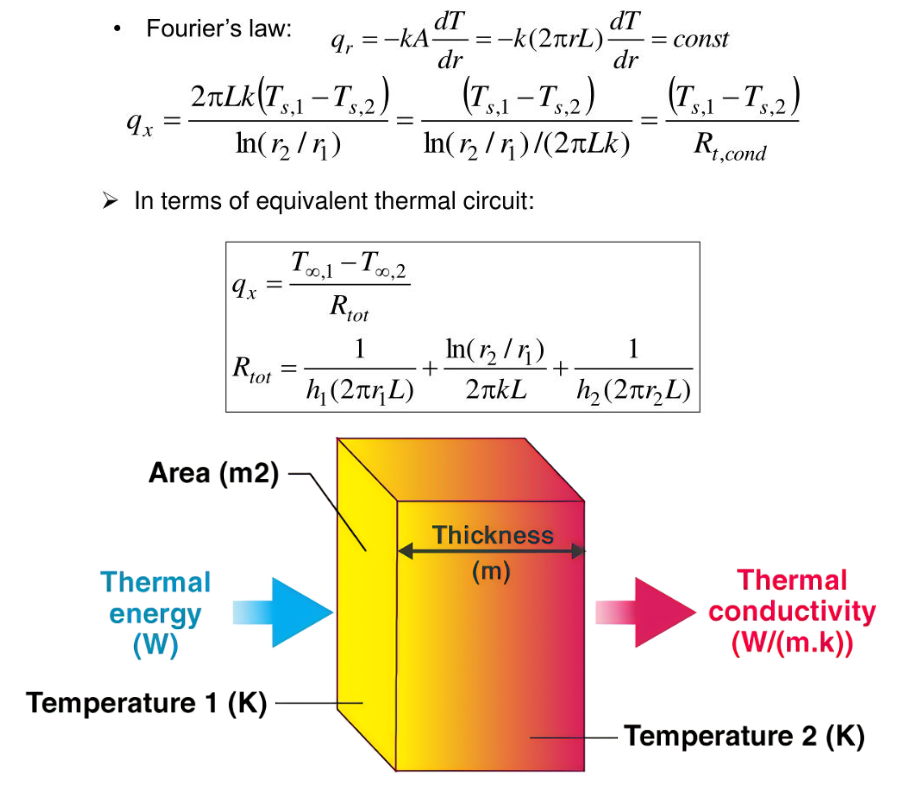
Definition: This converter transforms thermal resistance values between various units. Thermal resistance measures the opposition to heat flow through a material, typically in kelvin per watt (K/W).
Purpose: Useful in thermodynamics, heat transfer engineering, and building insulation for converting units in thermal calculations and R-value assessments.
The converter uses conversion factors relative to an arbitrary base (consistent with provided scaling):
Steps:
Thermal resistance conversion is critical for:
Example 1: Convert 1 degree Fahrenheit hour/Btu (IT) to kelvin/watt:
Result: 1.8956 kelvin/watt
Example 2: Convert 1 degree Fahrenheit hour/Btu (th) to kelvin/watt:
Result: 1.8969 kelvin/watt
Q: What is thermal resistance?
A: Thermal resistance is the measure of how well a material or system resists the flow of heat, analogous to electrical resistance, in units like K/W.
Q: Why are there different units for thermal resistance?
A: Units vary by system (SI vs. imperial) and definitions of Btu (IT vs. thermochemical), accommodating different engineering contexts.
Q: What is the difference between Btu (IT) and Btu (th)?
A: Btu (IT) is based on the international table (1055.05585262 J), while Btu (th) is thermochemical (1054.35026444 J), leading to slight differences in conversions.
Q: Why use seconds vs. hours in units?
A: Seconds are for instantaneous rates, while hours are common in steady-state or building applications where heat flow is per hour.
Q: Can this converter be used for all thermal resistance scenarios?
A: Yes, it handles conversions for common units in heat transfer and insulation calculations.