 Home
Home
 Back
Back
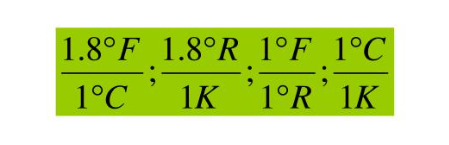
Definition: This converter transforms temperature interval (difference) values between various units. Temperature intervals measure differences in temperature, not absolute values, typically in kelvin (K) or degrees Celsius (°C).
Purpose: Useful in physics, engineering, meteorology, and thermodynamics for converting temperature differences without offsets used in absolute temperature conversions.
The converter uses conversion factors relative to an arbitrary base (consistent with provided scaling):
Steps:
Temperature interval conversion is critical for:
Example 1: Convert 1 degree Celsius to kelvin:
Result: 1 kelvin
Example 2: Convert 1 degree Fahrenheit to kelvin:
Result: 0.55556 kelvin
Q: What is a temperature interval?
A: A temperature interval is the difference between two temperatures, such as a change or gradient, without regard to absolute zero points.
Q: Why is this different from regular temperature conversion?
A: Regular conversions include offsets (e.g., +273.15 for Celsius to Kelvin), but intervals do not, as they represent differences.
Q: Why are Kelvin and Celsius intervals the same?
A: Both scales have the same size degree, so a 1 °C difference equals 1 K difference.
Q: How does Fahrenheit relate?
A: A 1 °F interval equals 5/9 K (approximately 0.55556 K).
Q: What is degree Reaumur?
A: An older scale where 1 °Re interval equals 1.25 K.
Q: Can this converter be used for absolute temperatures?
A: No, it's specifically for intervals; use a temperature converter for points with offsets.