 Home
Home
 Back
Back
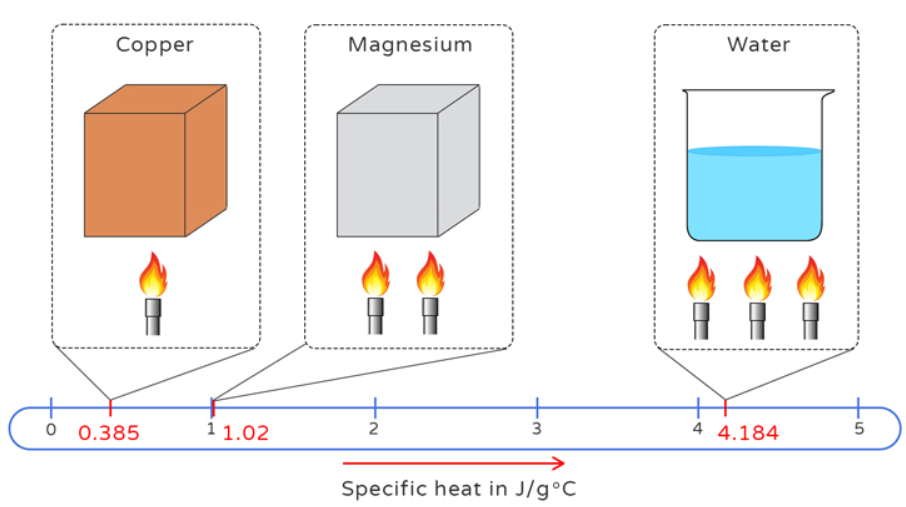
Definition: This converter transforms specific heat capacity values between various units. Specific heat capacity measures the heat energy required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree, typically in joule/kilogram/K (J/(kg*K)).
Purpose: Useful in thermodynamics, materials science, engineering, and chemistry for converting units in heat capacity calculations and thermal analysis.
The converter uses conversion factors relative to an arbitrary base (consistent with provided scaling):
Steps:
Specific heat capacity conversion is critical for:
Example 1: Convert 1 joule/kilogram/°C to joule/kilogram/K:
Result: 1 joule/kilogram/K
Example 2: Convert 1 calorie (IT)/gram/°C to joule/kilogram/K:
Result: 4186.8 joule/kilogram/K
Q: What is specific heat capacity?
A: Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1 K (or 1 °C), measured in J/(kg*K).
Q: Why are there different units for specific heat capacity?
A: Units vary by energy (joule, calorie, Btu), mass (kg, g, lb), and temperature scales (°C, K, °F, °R), reflecting different systems (SI, imperial).
Q: What is the difference between calorie (IT) and calorie (th)?
A: Calorie (IT) is based on the international table (4.1868 J), while calorie (th) is thermochemical (4.184 J), leading to slight differences.
Q: How are J/(kg*K) and cal/(g*°C) related?
A: 1 cal/(g*°C) ≈ 4186.8 J/(kg*K), as 1 cal = 4.1868 J and 1 g = 0.001 kg.
Q: Can this converter be used for all specific heat capacity scenarios?
A: Yes, it supports conversions for common units in thermal calculations across sciences and engineering.