 Home
Home
 Back
Back
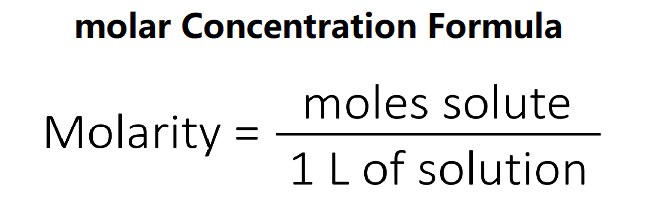
Definition: This converter transforms molar concentration values between various units. Molar concentration measures the amount of substance (in moles) per unit volume, typically in moles per liter (mol/L).
Purpose: Useful in chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology for converting concentration units in applications like solution preparation, reaction stoichiometry, and analytical measurements.
The converter uses conversion factors relative to the base unit kilomol/cubic millimeter [kmol/mm3]:
Steps:
Molar concentration conversion is critical for:
Example 1: Convert 1 mol/liter to mol/cubic meter:
Result: 1000 mol/cubic meter
Example 2: Convert 1 millimol/liter to mol/liter:
Result: 1.0000e-3 mol/liter
Q: What is molar concentration?
A: Molar concentration is the amount of a substance (in moles) dissolved in a given volume of solution, typically measured in moles per liter (mol/L).
Q: Why are there different units for molar concentration?
A: Different scales and contexts in chemistry require units varying by prefixes (milli-, kilo-) and volume units (liter, cubic meter, etc.) for precision and convenience.
Q: How are mol/L and mol/m3 related?
A: One mol/L is equal to 1000 mol/m3.
Q: Can this converter be used for all molar concentration scenarios?
A: Yes, it converts units of molar concentration, applicable to any scenario involving substance amount per volume.