 Home
Home
 Back
Back
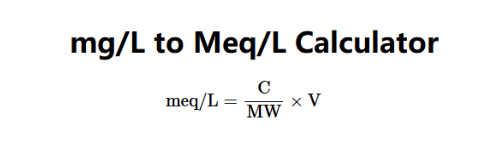
The Mg/L to Meq/L Converter calculates the concentration in milliequivalents per liter (meq/L) from concentration, molecular weight, and valence using the following formula:
Where:
Select the units for concentration (mg/L, g/L, μg/L) and molecular weight (g/mol, kg/mol, mg/mol), then enter the values and valence to calculate meq/L.
This converter is useful in chemistry and environmental science for converting mass-based concentrations to ion-based concentrations in meq/L.
Input the concentration with its unit (mg/L, g/L, or μg/L), molecular weight with its unit (g/mol, kg/mol, or mg/mol), and valence. The calculator converts all inputs to mg/L and g/mol, then computes the meq/L.
Example: Convert 0.04008 g/L of calcium (Ca²⁺) to meq/L, with a molecular weight of 40.08 g/mol and valence of 2.
Use this tool for accurate conversions.
Reference conversions for common ions (all in base units: mg/L and g/mol):
| Ion | Concentration (mg/L) | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Valence | meq/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na⁺ | 22.99 | 22.99 | 1 | 1.000 |
| Ca²⁺ | 40.08 | 40.08 | 2 | 2.000 |
| Mg²⁺ | 24.31 | 24.31 | 2 | 2.000 |
| Cl⁻ | 177.25 | 35.45 | 1 | 5.000 |
| HCO₃⁻ | 183.03 | 61.01 | 1 | 3.000 |
Adjust units as needed using the form dropdowns.
Below are frequently asked questions about Mg/L to Meq/L conversions: