 Home
Home
 Back
Back
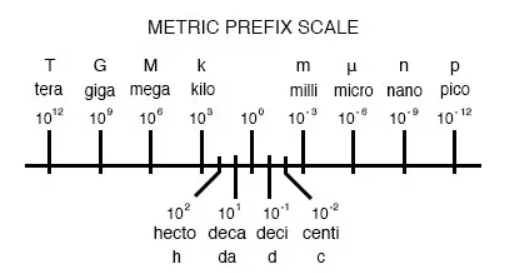
Definition: This converter transforms values between different SI metric prefixes. Prefixes are multipliers used with base units to denote powers of ten, from yotta (10^24) to yocto (10^-24).
Purpose: Useful in science, engineering, and computing for converting quantities expressed with different prefixes, simplifying large or small numbers.
The converter uses conversion factors relative to an arbitrary base ('none' = 1):
Steps:
Metric prefix conversion is critical for:
Example 1: Convert 1 yotta to none:
Result: 1.0e+24 none
Example 2: Convert 1 mega to kilo:
Result: 1000 kilo
Q: What are metric prefixes?
A: Metric prefixes are symbols added to base units to indicate multiples or fractions of 10, like kilo (10^3) or milli (10^-3).
Q: Why convert between prefixes?
A: To standardize measurements or simplify expressions for very large/small values.
Q: Is 'none' a prefix?
A: 'None' represents no prefix, the base value (multiplier 1).
Q: How do positive and negative exponents work?
A: Positive (e.g., yotta 10^24) for large multiples; negative (e.g., yocto 10^-24) for small fractions.
Q: Can this converter be used with any unit?
A: Yes, it converts the multiplier part; apply to any base unit like meters, grams.