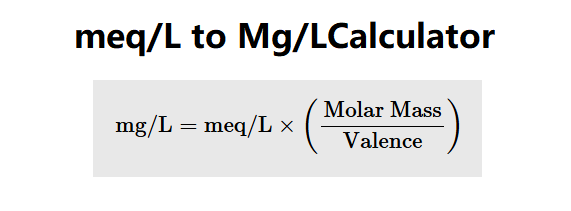Meq/L to Mg/L Calculator
How to Convert Meq/L to Mg/L
The Meq/L to Mg/L Converter calculates the concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L) from milliequivalents per liter (meq/L), molar mass, and valence using the following formula:
\( \text{mg/L} = \text{meq/L} \times \frac{\text{Molar Mass}}{\text{Valence}} \)
Where:
- \( \text{meq/L} \): Milliequivalents per liter, a measure of chemical concentration based on the number of equivalents.
- \( \text{Molar Mass} \): The mass of one mole of the substance in grams per mole (g/mol).
- \( \text{Valence} \): The number of equivalents per mole of the substance (unitless, typically an integer like 1 or 2).
- \( \text{mg/L} \): Milligrams per liter, a measure of mass concentration.
Enter the milliequivalents per liter, molar mass, and valence to calculate the concentration in mg/L.
Using the Meq/L to Mg/L Converter
This converter is useful in chemistry, environmental science, and water treatment for converting ionic concentrations from meq/L to mg/L.
Input the milliequivalents per liter (meq/L), molar mass (g/mol), and valence. The calculator will compute the concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L).
Example: Convert 2 meq/L of calcium (Ca²⁺) to mg/L, with a molar mass of 40.08 g/mol and valence of 2.
- Milliequivalents per Liter: \( 2 \, \text{meq/L} \)
- Molar Mass: \( 40.08 \, \text{g/mol} \)
- Valence: \( 2 \)
- mg/L: \( 2 \times \frac{40.08}{2} = 2 \times 20.04 = 40.08 \, \text{mg/L} \)
- Result: \( 2 \, \text{meq/L} = 40.08 \, \text{mg/L} \)
Use this tool for accurate conversions in chemical and environmental calculations.
Common Conversion Table
The following table provides quick reference conversions for meq/L to mg/L for common ions, using their typical molar mass and valence:
| Ion |
meq/L |
Molar Mass (g/mol) |
Valence |
mg/L |
| Na⁺ |
1 |
22.99 |
1 |
22.99 |
| Ca²⁺ |
2 |
40.08 |
2 |
40.08 |
| Mg²⁺ |
1 |
24.31 |
2 |
12.155 |
| Cl⁻ |
5 |
35.45 |
1 |
177.25 |
| HCO₃⁻ |
3 |
61.01 |
1 |
183.03 |
Use this table for quick lookups or to verify calculator results for common ions.
Common FAQ
Below are frequently asked questions about Meq/L to Mg/L conversions:
- Q: What is meq/L?
A: Milliequivalents per liter (meq/L) measures the concentration of ions based on their chemical reactivity, accounting for valence.
- Q: Why do I need molar mass and valence?
A: Molar mass (g/mol) defines the mass of one mole of the substance, and valence indicates the number of equivalents per mole, both essential for the conversion to mg/L.
- Q: Can negative values be used?
A: Negative meq/L or molar mass values are not physically meaningful. Valence must be a positive integer (typically 1 or higher). The calculator enforces these constraints.
- Q: How accurate is this converter?
A: The converter uses the exact formula and provides results rounded to 6 decimal places for precision.
- Q: What are common molar masses and valences?
A: Examples include Na⁺ (22.99 g/mol, valence 1), Ca²⁺ (40.08 g/mol, valence 2), Cl⁻ (35.45 g/mol, valence 1). Refer to the conversion table for more.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back