1. What is Taper Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the taper per unit length (\( \text{TPI} \)) and taper angle (\( \theta \)) for a conical workpiece based on the major diameter (\( D_1 \)), minor diameter (\( D_s \)), and taper length (\( T_1 \)).
Purpose: It helps machinists and engineers determine the taper characteristics for designing or machining tapered components, ensuring proper fit and function.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following equations:
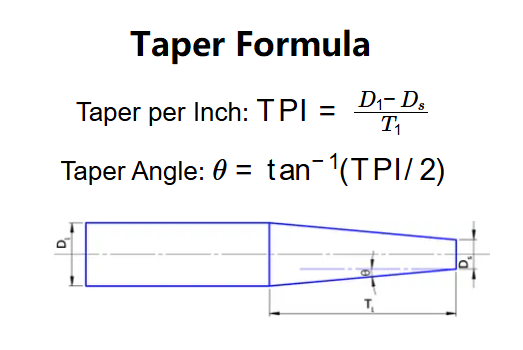
- Taper per Inch: \( \text{TPI} = \frac{D_1 - D_s}{T_1} \)
- Taper Angle: \( \theta = \tan^{-1}(\text{TPI}/2) \)
Where:
- \( D_1 \): Major diameter (converted to mm);
- \( D_s \): Minor diameter (converted to mm);
- \( T_1 \): Taper length (converted to inches for base TPI calculation);
- \( \text{TPI} \): Taper per unit length (converted to selected unit: in/in, in/ft, in/yd, mm/mm, mm/cm, mm/m);
- \( \theta \): Taper angle (in degrees).
Steps:
- Enter the major diameter and select its unit (mm, cm, m, km, in, ft, yd, mi, nmi).
- Enter the minor diameter and select its unit (mm, cm, m, km, in, ft, yd, mi, nmi).
- Enter the taper length and select its unit (mm, cm, m, km, in, ft, yd, mi, nmi).
- Click "Calculate" to compute the taper and taper angle.
- Select the desired unit for the taper result.
- Results are displayed with 4 decimal places or in scientific notation if less than 0.001.
3. Importance of Taper Calculation
Calculating taper is crucial for:
- Precision: Ensures accurate machining of tapered components for proper fit in assemblies.
- Design: Helps in designing components like tool shanks, fittings, or conical parts.
- Compatibility: Matches tapers to standard specifications (e.g., Morse taper, Jacobs taper).
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1: Calculate the taper for a workpiece:
- Major Diameter: 100 mm;
- Minor Diameter: 80 mm;
- Taper Length: 50 mm (1.9685 in);
- Base TPI: \( \text{TPI} = \frac{100 - 80}{1.9685} \approx 10.1604 \, \text{in/in} \);
- In mm/cm: \( 10.1604 / 2.54 \approx 4.0002 \, \text{mm/cm} \);
- Taper Angle: \( \theta = \tan^{-1}(10.1604/2) \approx 78.9469 \, \text{degrees} \);
- Result: Taper = 4.0002 mm/cm, Taper Angle = 78.9469 degrees (if mm/cm selected).
Example 2: Calculate the taper for another setup:
- Major Diameter: 5 in (127 mm);
- Minor Diameter: 4 in (101.6 mm);
- Taper Length: 2 in (50.8 mm);
- Base TPI: \( \text{TPI} = \frac{127 - 101.6}{2} \approx 12.7000 \, \text{in/in} \);
- In in/ft: \( 12.7000 \times 12 \approx 152.4000 \, \text{in/ft} \);
- Taper Angle: \( \theta = \tan^{-1}(12.7000/2) \approx 81.1086 \, \text{degrees} \);
- Result: Taper = 152.4000 in/ft, Taper Angle = 81.1086 degrees (if in/ft selected).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is Taper per Unit Length?
A: Taper per unit length (\( \text{TPI} \)) is the reduction in the cross-sectional diameter per unit length along the taper, expressed in units like in/in, mm/cm, etc.
Q: Why is taper angle important?
A: The taper angle (\( \theta \)) defines the slope of the taper, which is critical for ensuring proper fit and alignment in machining applications.
Q: Can this calculator be used for all types of tapers?
A: Yes, it can be used for any conical taper as long as the major diameter, minor diameter, and taper length are provided.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back