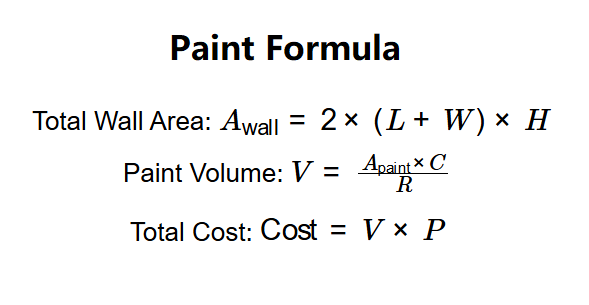1. What is the Paint Calculator?
Definition: This calculator estimates the volume of paint required to cover the walls of a room and the associated cost, based on room dimensions, door and window sizes, number of doors and windows, number of coats, and paint coverage rate.
Purpose: It assists homeowners, DIY enthusiasts, and contractors in planning painting projects by determining the exact amount of paint needed, preventing over- or under-purchasing, and optionally calculating the total cost.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following equations:
- Total Wall Area: \( A_{\text{wall}} = 2 \times (L + W) \times H \)
- Paintable Area: \( A_{\text{paint}} = A_{\text{wall}} - (N_{\text{doors}} \times H_{\text{door}} \times W_{\text{door}}) - (N_{\text{windows}} \times H_{\text{window}} \times W_{\text{window}}) \)
- Paint Volume: \( V = \frac{A_{\text{paint}} \times C}{R} \)
- Total Cost: \( \text{Cost} = V \times P \)
Where:
- \( L \): Room length (cm, m, in, ft, or yd);
- \( W \): Room width (cm, m, in, ft, or yd);
- \( H \): Room height (cm, m, in, ft, or yd);
- \( H_{\text{door}} \): Door height (cm, m, in, ft, or yd);
- \( W_{\text{door}} \): Door width (cm, m, in, ft, or yd);
- \( H_{\text{window}} \): Window height (cm, m, in, ft, or yd);
- \( W_{\text{window}} \): Window width (cm, m, in, ft, or yd);
- \( N_{\text{doors}} \): Number of doors;
- \( N_{\text{windows}} \): Number of windows;
- \( C \): Number of paint coats;
- \( R \): Paint coverage rate (m²/liter or ft²/gallon);
- \( V \): Paint volume needed (liters or gallons);
- \( P \): Cost per unit volume ($/liter or $/gallon).
Steps:
- Enter the room dimensions (length, width, height) and select their units (cm, m, in, ft, or yd).
- Enter the door height and width, and select their units (cm, m, in, ft, or yd).
- Enter the number of doors.
- Enter the window height and width, and select their units (cm, m, in, ft, or yd).
- Enter the number of windows.
- Enter the number of paint coats (default is 2).
- Enter the paint coverage rate and select its unit (m²/liter or ft²/gallon).
- Optionally, enter the cost per unit volume and select its unit ($/liter or $/gallon).
- Convert all dimensions to meters and calculate the total wall area.
- Subtract the areas of doors and windows to get the paintable area.
- Calculate the paint volume by dividing the paintable area times the number of coats by the coverage rate.
- Convert the paint volume to the selected output unit (liters or gallons).
- If cost is provided, calculate the total cost by multiplying the paint volume by the cost per unit volume.
- Display results, formatted in scientific notation if the absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Paint Calculation
Calculating the correct amount of paint is crucial for:
- Cost Efficiency: Avoids purchasing excess paint or running short during the project.
- Time Savings: Ensures the project is completed without interruptions for additional paint runs.
- Environmental Impact: Reduces paint waste, promoting sustainable practices.
- Quality: Ensures sufficient paint for even coverage, especially with multiple coats.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1 (Metric Units): Calculate the paint needed for a room with metric units:
- Room Dimensions: \( L = 500 \, \text{cm}, W = 400 \, \text{cm}, H = 300 \, \text{cm} \);
- Door: \( H_{\text{door}} = 200 \, \text{cm}, W_{\text{door}} = 80 \, \text{cm}, N_{\text{doors}} = 1 \);
- Window: \( H_{\text{window}} = 100 \, \text{cm}, W_{\text{window}} = 120 \, \text{cm}, N_{\text{windows}} = 2 \);
- Coats: 2;
- Coverage Rate: \( 10 \, \text{m}^2/\text{liter} \);
- Cost: \( \$5/\text{liter} \);
- Output Unit: Liters;
- Total Wall Area: \( 2 \times (5 + 4) \times 3 = 54 \, \text{m}^2 \);
- Paintable Area: \( 54 - (1 \times 2.0 \times 0.8) - (2 \times 1.0 \times 1.2) = 50 \, \text{m}^2 \);
- Paint Volume: \( \frac{50 \times 2}{10} = 10 \, \text{liters} \);
- Total Cost: \( 10 \times 5 = 50 \, \$ \);
- Result: \( V = 10.0000 \, \text{liters}, \text{Cost} = 50.0000 \, \$ \).
Example 2 (Imperial Units): Calculate the paint needed with imperial units:
- Room Dimensions: \( L = 16 \, \text{ft}, W = 12 \, \text{ft}, H = 8 \, \text{ft} \);
- Door: \( H_{\text{door}} = 80 \, \text{in}, W_{\text{door}} = 32 \, \text{in}, N_{\text{doors}} = 2 \);
- Window: \( H_{\text{window}} = 36 \, \text{in}, W_{\text{window}} = 24 \, \text{in}, N_{\text{windows}} = 1 \);
- Coats: 2;
- Coverage Rate: \( 400 \, \text{ft}^2/\text{gallon} \);
- Cost: \( \$30/\text{gallon} \);
- Output Unit: Gallons;
- Total Wall Area: \( 2 \times (4.8768 + 3.6576) \times 2.4384 = 41.806 \, \text{m}^2 \);
- Paintable Area: \( 41.806 - (2 \times 2.032 \times 0.8128) - (1 \times 0.9144 \times 0.6096) \approx 37.951 \, \text{m}^2 \);
- Paint Volume: \( \frac{37.951 \times 2}{10.5673} \approx 7.184 \, \text{liters} \approx 1.8977 \, \text{gallons} \);
- Total Cost: \( 1.8977 \times 30 \approx 56.931 \, \$ \);
- Result: \( V = 1.8977 \, \text{gallons}, \text{Cost} = 56.9310 \, \$ \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Does this calculator include the ceiling?
A: No, it calculates paint for walls only. To include the ceiling, you would need to add its area manually to the total wall area.
Q: Why are door and window areas subtracted?
A: Doors and windows are typically not painted, so their areas are excluded to estimate the actual paintable surface accurately.
Q: How accurate is the paint volume estimate?
A: The estimate assumes flat, non-porous surfaces. For rough or porous surfaces, add up to 20% more paint. Always buy 10% extra for waste and touch-ups.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back