1. What is Carbon Equivalent Calculator?
Definition: This calculator determines the carbon equivalent (CE) or critical metal parameter (Pcm) of steel based on the weight percentages of alloying elements, aiding in assessing the steel's weldability.
Purpose: It is used in metallurgy and welding to predict the likelihood of hydrogen-induced cold cracking, helping engineers and welders decide on preheating requirements and welding techniques.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following equations:
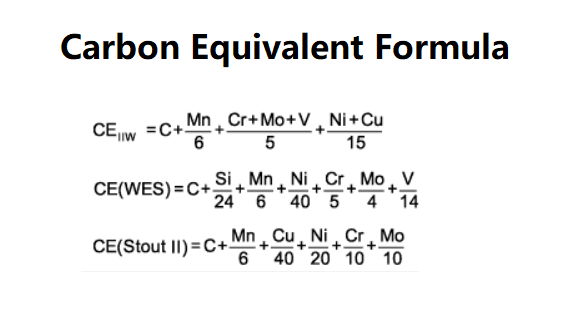
- \( \text{CE (IIW)} = C + \frac{Mn}{6} + \frac{Cu + Ni}{15} + \frac{Cr + Mo + V}{5} \)
- \( \text{CE (AWS)} = C + \frac{Mn + Si}{6} + \frac{Cr + Mo + V}{5} + \frac{Cu + Ni}{15} \)
- \( \text{Pcm (JWES)} = C + \frac{Si}{30} + \frac{Mn + Cu + Cr}{20} + \frac{Ni}{60} + \frac{Mo}{15} + \frac{V}{10} + 5B \)
- \( \text{CE (JWES)} = C + \frac{Si}{24} + \frac{Mn}{6} + \frac{Ni}{40} + \frac{Cr}{5} + \frac{Mo}{4} + \frac{V}{14} \)
Where:
- \( C \): Carbon percentage (%);
- \( Mn \): Manganese percentage (%);
- \( Si \): Silicon percentage (%);
- \( Cu \): Copper percentage (%);
- \( Ni \): Nickel percentage (%);
- \( Cr \): Chromium percentage (%);
- \( Mo \): Molybdenum percentage (%);
- \( V \): Vanadium percentage (%);
- \( B \): Boron percentage (%).
Steps:
- Select the formula type (IIW, AWS, JWES Pcm, or JWES CE).
- Enter the weight percentages of alloying elements (\( C \), \( Mn \), \( Si \), \( Cu \), \( Ni \), \( Cr \), \( Mo \), \( V \)).
- If JWES Pcm is selected, enter the Boron percentage (\( B \)).
- Validate inputs: Ensure \( C \leq 2.14\% \) and all percentages are non-negative.
- Calculate CE or Pcm using the selected formula.
- Assess weldability:
- For CE formulas (IIW, AWS, JWES CE):
- CE ≤ 0.40%: Very Good (No preheating).
- 0.40% < CE ≤ 0.60%: Moderate (Preheating may be required).
- CE > 0.60%: Poor (Preheating compulsory).
- For Pcm (JWES Pcm):
- Pcm ≤ 0.30%: Very Good (No preheating).
- 0.30% < Pcm ≤ 0.50%: Moderate (Preheating may be required).
- Pcm > 0.50%: Poor (Preheating compulsory).
- Display results: CE or Pcm value and weldability assessment.
3. Importance of Carbon Equivalent Calculation
Calculating carbon equivalent or Pcm is crucial for:
- Weldability Prediction: Determines the risk of cold cracking, guiding welding procedures.
- Material Selection: Helps choose steels with suitable properties for specific applications.
- Cost Efficiency: Avoids unnecessary preheating or overly conservative welding practices.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1 (JWES Pcm Formula): Calculate Pcm for a steel alloy:
- Composition: \( C = 0.18\% \), \( Si = 0.30\% \), \( Mn = 1.0\% \), \( Cu = 0.02\% \), \( Ni = 0.01\% \), \( Cr = 0.05\% \), \( Mo = 0.01\% \), \( V = 0.01\% \), \( B = 0.0005\% \);
- Formula: \( \text{Pcm} = C + \frac{Si}{30} + \frac{Mn + Cu + Cr}{20} + \frac{Ni}{60} + \frac{Mo}{15} + \frac{V}{10} + 5B \);
- Calculation: \( \text{Pcm} = 0.18 + \frac{0.30}{30} + \frac{1.0 + 0.02 + 0.05}{20} + \frac{0.01}{60} + \frac{0.01}{15} + \frac{0.01}{10} + 5 \times 0.0005 \);
- \( \text{Pcm} = 0.18 + 0.01 + \frac{1.07}{20} + \frac{0.01}{60} + \frac{0.01}{15} + \frac{0.01}{10} + 0.0025 \);
- \( \text{Pcm} = 0.18 + 0.01 + 0.0535 + 0.0001667 + 0.0006667 + 0.001 + 0.0025 \approx 0.2478 \);
- Weldability: Pcm ≈ 0.2478% (Very Good, no preheating required);
- Result: Pcm = 0.2478%, Weldability: Very Good.
Example 2 (JWES CE Formula): Calculate CE for AISI 1018 steel:
- Composition: \( C = 0.20\% \), \( Si = 0.25\% \), \( Mn = 0.90\% \), \( Ni = 0\% \), \( Cr = 0\% \), \( Mo = 0\% \), \( V = 0\% \);
- Formula: \( \text{CE} = C + \frac{Si}{24} + \frac{Mn}{6} + \frac{Ni}{40} + \frac{Cr}{5} + \frac{Mo}{4} + \frac{V}{14} \);
- Calculation: \( \text{CE} = 0.20 + \frac{0.25}{24} + \frac{0.90}{6} + \frac{0}{40} + \frac{0}{5} + \frac{0}{4} + \frac{0}{14} \);
- \( \text{CE} = 0.20 + 0.0104167 + 0.15 + 0 \approx 0.3604 \);
- Weldability: CE ≈ 0.3604% (Very Good, no preheating required);
- Result: CE = 0.3604%, Weldability: Very Good.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the difference between Pcm and CE formulas?
A: Pcm (JWES) focuses on critical metal parameters for high-strength steels, including Boron, with lower thresholds for weldability. CE formulas (IIW, AWS, JWES CE) are more general and assess overall hardenability.
Q: Why are Boron percentages typically very small?
A: Boron is a potent hardenability agent; even small amounts (e.g., 0.0005%) significantly affect steel properties, which is why the Pcm formula multiplies it by 5.
Q: Can this calculator be used for all steel types?
A: It is designed for carbon and low-alloy steels. High-alloy or stainless steels may require different formulas not covered here.
Carbon Equivalent Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back