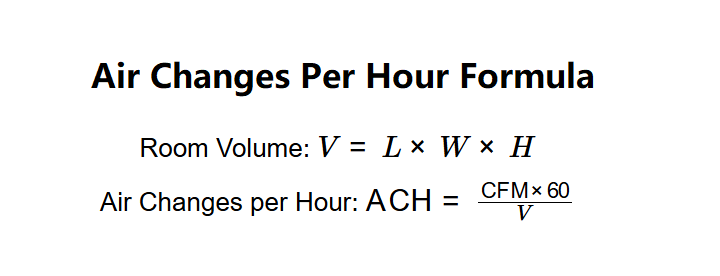1. What is the Air Changes per Hour Calculator?
Definition: This calculator determines the Air Changes per Hour (ACH), a measure of how many times the air in a room is replaced per hour, based on the room’s volume and the ventilation system’s airflow rate (CFM).
Purpose: It is used in HVAC design, indoor air quality assessment, and building management to ensure adequate ventilation for health, comfort, and safety.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following equations:
- Room Volume: \( V = L \times W \times H \)
- Air Changes per Hour: \( \text{ACH} = \frac{\text{CFM} \times 60}{V} \)
Where:
- \( V \): Room volume (mm³, cm³, m³, in³, ft³, yd³);
- \( L \): Room length (m, cm, mm, in, ft, yd);
- \( W \): Room width (m, cm, mm, in, ft, yd);
- \( H \): Room height (m, cm, mm, in, ft, yd);
- \( \text{CFM} \): Airflow rate (ft³/min, m³/min);
- \( \text{ACH} \): Air changes per hour (dimensionless).
Steps:
- Enter the room’s length, width, and height with their units.
- Enter the airflow rate (CFM) of the ventilation device with its unit.
- Convert dimensions to meters and CFM to m³/min for calculation.
- Calculate the room volume (\( V = L \times W \times H \)).
- Compute ACH (\( \text{ACH} = \frac{\text{CFM} \times 60}{V} \)).
- Convert volume to the selected output unit and display results, formatted in scientific notation if the absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of ACH Calculation
Calculating ACH is crucial for:
- Indoor Air Quality: Ensures sufficient fresh air to dilute pollutants, odors, and CO₂.
- Health and Safety: Meets ventilation standards for homes, offices, or healthcare facilities.
- HVAC Design: Helps size ventilation systems to achieve desired air change rates.
- Energy Efficiency: Balances ventilation needs with energy consumption for heating or cooling.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1 (Imperial Units - Office Room): Calculate the ACH for an office with a ventilation system:
- Length: \( L = 20 \, \text{ft} \approx 6.096 \, \text{m} \);
- Width: \( W = 15 \, \text{ft} \approx 4.572 \, \text{m} \);
- Height: \( H = 8 \, \text{ft} \approx 2.4384 \, \text{m} \);
- Airflow Rate: \( \text{CFM} = 500 \, \text{ft}^3/\text{min} \approx 14.1584 \, \text{m}^3/\text{min} \);
- Volume: \( V = 6.096 \times 4.572 \times 2.4384 \approx 67.968 \, \text{m}^3 \approx 2400 \, \text{ft}^3 \);
- ACH: \( \text{ACH} = \frac{14.1584 \times 60}{67.968} \approx 12.5 \);
- Result: \( V = 2400.0000 \, \text{ft}^3 \), \( \text{ACH} = 12.5000 \).
Example 2 (Metric Units - Classroom): Calculate the ACH for a classroom with a ventilation system:
- Length: \( L = 10 \, \text{m} \);
- Width: \( W = 8 \, \text{m} \);
- Height: \( H = 3 \, \text{m} \);
- Airflow Rate: \( \text{CFM} = 20 \, \text{m}^3/\text{min} \);
- Volume: \( V = 10 \times 8 \times 3 = 240 \, \text{m}^3 \);
- ACH: \( \text{ACH} = \frac{20 \times 60}{240} = 5 \);
- Result: \( V = 240.0000 \, \text{m}^3 \), \( \text{ACH} = 5.0000 \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a typical ACH value?
A: Typical ACH values vary: 0.5–2 for homes, 4–8 for offices, and 10–20 for hospitals or cleanrooms, depending on ventilation needs.
Q: Where do I find the CFM of my ventilation device?
A: Check the device’s specifications, manual, or label, often listed as CFM (ft³/min) or m³/h (convert m³/h to m³/min by dividing by 60).
Q: Does room shape affect the calculation?
A: This calculator assumes a rectangular prism. For irregular shapes, estimate the volume by breaking it into rectangular sections or using an average height.
Air Changes per Hour Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back