 Home
Home
 Back
Back
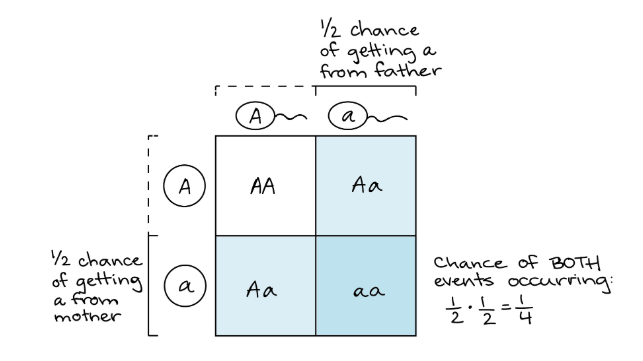
Definition: This calculator computes the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of offspring from a monohybrid cross (single trait), using a Punnett square to predict inheritance patterns under Mendelian genetics.
Purpose: It is used in genetics to predict the likelihood of offspring inheriting specific genotypes and phenotypes for a single trait, helping to understand basic inheritance patterns.
The calculator applies Mendelian genetics principles, assuming:
Steps:
Calculating Punnett square outcomes is crucial for:
Example 1: Calculate the genotypic and phenotypic ratios for a cross between two Aa parents:
Example 2: Calculate the genotypic and phenotypic ratios for a cross between AA and aa:
Q: What is a Punnett square?
A: A Punnett square is a diagrammatic tool used in genetics to predict the possible genotypes of offspring from a particular cross, named after Reginald C. Punnett who devised it in 1905.
Q: Why does the phenotypic ratio often show 3:1 in a heterozygous cross?
A: In a monohybrid cross between two heterozygous individuals (e.g., Aa × Aa) under complete dominance, the phenotypic ratio is 3:1 because three out of four offspring inherit at least one dominant allele (A-, showing the dominant trait), while one inherits two recessive alleles (aa, showing the recessive trait).
Q: What if the trait does not follow complete dominance?
A: This calculator assumes complete dominance. If the trait exhibits incomplete dominance or codominance (e.g., AB blood type), the phenotypic outcomes would differ, and a modified approach would be needed.