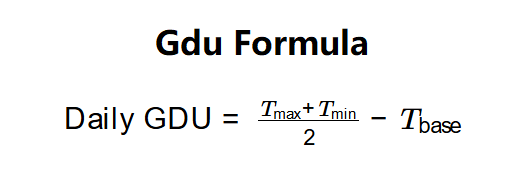1. What is the Growing Degree Units (GDU) Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the Growing Degree Units (GDUs), a measure of accumulated heat units that drive crop development and growth, based on daily temperatures and the number of days since planting.
Purpose: It helps farmers predict crop development stages, optimize planting schedules, and plan harvests by quantifying the heat available over a growing period.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following equations:
- \( \text{Daily GDU} = \frac{T_{\text{max}} + T_{\text{min}}}{2} - T_{\text{base}} \)
- \( \text{Total GDU} = \text{Daily GDU} \times \text{Days Since Planting} \)
Where:
- \( T_{\text{max}} \): Daily maximum temperature (converted to °C if in °F, capped at 30°C);
- \( T_{\text{min}} \): Daily minimum temperature (converted to °C if in °F, floored at base temp);
- \( T_{\text{base}} \): Base temperature (converted to °C if in °F, typically 10°C for corn);
- Daily GDU is set to 0 if the result is negative;
- Total GDU accumulates daily GDUs over the specified number of days.
Steps:
- Enter the daily maximum temperature (\( T_{\text{max}} \)) and select its unit (°C or °F).
- Enter the daily minimum temperature (\( T_{\text{min}} \)) and select its unit (°C or °F).
- Enter the base temperature (\( T_{\text{base}} \)) and select its unit (°C or °F, default 10°C).
- Enter the number of days since planting.
- Convert each temperature to °C based on its selected unit, apply limits (max 30°C, min = base temp).
- Calculate daily GDU using the formula above.
- Calculate total GDU by multiplying daily GDU by the number of days.
- Display the results as numeric values, with the unit (GDU) shown in labels.
3. Importance of GDU Calculation
Calculating GDUs is crucial for:
- Crop Development: GDUs predict key growth stages like emergence (100 GDUs for corn, 130 for soybeans), silking, and maturity, aiding in crop management [Web ID: 22].
- Climate Adaptation: Helps farmers select regions or microclimates best suited for crops by analyzing heat availability [Web ID: 1].
- Risk Management: Allows preparation for adverse conditions, reducing crop failure and financial loss by anticipating growth stages [Web ID: 1].
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1 (Mixed Units, Corn): Calculate GDUs for a corn field:
- Daily Maximum Temperature: \( T_{\text{max}} = 77 \, \text{°F} \), convert to °C: \( (77 - 32) \times \frac{5}{9} = 25 \, \text{°C} \);
- Daily Minimum Temperature: \( T_{\text{min}} = 15 \, \text{°C} \);
- Base Temperature: \( T_{\text{base}} = 50 \, \text{°F} \), convert to °C: \( (50 - 32) \times \frac{5}{9} = 10 \, \text{°C} \);
- Days Since Planting: 5 days;
- Daily GDU: \( \frac{25 + 15}{2} - 10 = 20 - 10 = 10 \, \text{GDU} \);
- Total GDU: \( 10 \times 5 = 50 \, \text{GDU} \);
- Result: Daily GDU = 10.0000, Total GDU = 50.0000 (unit: GDU).
Example 2 (Celsius, Corn with Limits): Calculate GDUs for a corn field:
- Daily Maximum Temperature: \( T_{\text{max}} = 35 \, \text{°C} \), capped at 30°C;
- Daily Minimum Temperature: \( T_{\text{min}} = 45 \, \text{°F} \), convert to °C: \( (45 - 32) \times \frac{5}{9} \approx 7.22 \, \text{°C} \);
- Base Temperature: \( T_{\text{base}} = 10 \, \text{°C} \);
- Min Temp (adjusted): 7.22°C < 10°C, so use 10°C;
- Days Since Planting: 4 days;
- Daily GDU: \( \frac{30 + 10}{2} - 10 = 20 - 10 = 10 \, \text{GDU} \);
- Total GDU: \( 10 \times 4 = 40 \, \text{GDU} \);
- Result: Daily GDU = 10.0000, Total GDU = 40.0000 (unit: GDU).
Example 3 (Fahrenheit, Image Case): Calculate GDUs based on the image inputs:
- Daily Maximum Temperature: \( T_{\text{max}} = 25 \, \text{°F} \), convert to °C: \( (25 - 32) \times \frac{5}{9} \approx -3.89 \, \text{°C} \);
- Daily Minimum Temperature: \( T_{\text{min}} = 10 \, \text{°F} \), convert to °C: \( (10 - 32) \times \frac{5}{9} \approx -12.22 \, \text{°C} \);
- Base Temperature: \( T_{\text{base}} = 50 \, \text{°F} \), convert to °C: \( (50 - 32) \times \frac{5}{9} = 10 \, \text{°C} \);
- Min Temp (adjusted): -12.22°C < 10°C, so use 10°C;
- Daily GDU: \( \frac{-3.89 + 10}{2} - 10 = \frac{6.11}{2} - 10 = 3.055 - 10 = -6.945 \), set to 0 since negative;
- Days Since Planting: Not specified in the image, but assume 1 day for daily GDU;
- Total GDU: \( 0 \times 1 = 0 \, \text{GDU} \);
- Result: Daily GDU = 0.0000, Total GDU = 0.0000 (unit: GDU).
- Note: The image shows a GDU of 12.5, which does not align with the standard formula. The correct Daily GDU should be 0, as temperatures are below the base temperature after adjustments.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can I use different units for each temperature input?
A: Yes, the calculator allows independent unit selection for maximum, minimum, and base temperatures (°C or °F). Each temperature is converted to °C for calculation to ensure consistency.
Q: What is the base temperature for corn?
A: The base temperature for corn is typically 10°C (50°F), below which growth does not occur [Web ID: 1].
Q: Why cap the maximum temperature at 30°C (86°F)?
A: Above 30°C (86°F), corn growth does not increase significantly as the plant enters survival mode rather than developmental growth [Web ID: 22].
Growing Degree Units (GDU) Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back