1. What is the Cell Doubling Time Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the doubling time (\( t_d \)) and growth rate (\( r \)) of a cell population, where doubling time is the time required for the population to double in size, and growth rate is the proportional increase per unit time.
Purpose: It is used in biology and microbiology to study cell proliferation rates, which is critical for understanding growth dynamics in cell cultures, microbial studies, and cancer research.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
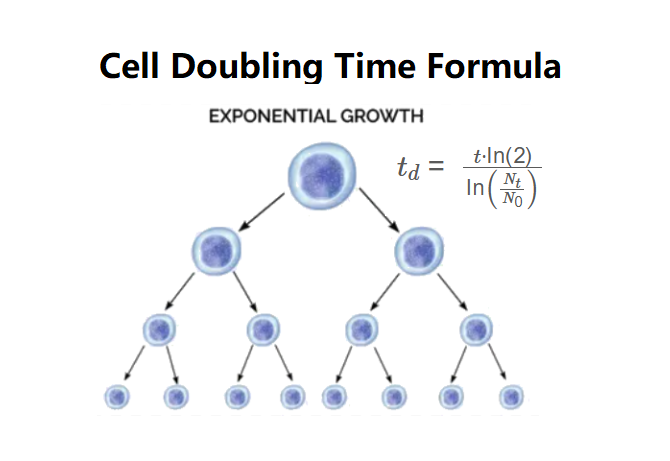
- \( k = \frac{\ln \left( \frac{N_t}{N_0} \right)}{t} \)
- \( r = e^k - 1 \)
- \( t_d = \frac{\ln(2)}{k} \)
Where:
- \( N_0 \): Initial concentration (cells/mL, cells/L);
- \( N_t \): Final concentration after time \( t \) (cells/mL, cells/L);
- \( t \): Duration of growth (min, hr, day);
- \( k \): Growth rate constant (per hour);
- \( r \): Growth rate (unitless);
- \( t_d \): Doubling time (min, hr, day).
Steps:
- Enter the initial concentration (\( N_0 \)) with its unit.
- Enter the final concentration (\( N_t \)) with its unit.
- Enter the duration (\( t \)) with its unit.
- Convert all units to a consistent base (cells/mL for concentration, hours for duration).
- Calculate the growth rate constant \( k \), then the growth rate \( r \), and doubling time \( t_d \).
- Convert the doubling time to the selected output unit and display both results, formatted in scientific notation if the absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Cell Doubling Time Calculation
Calculating the doubling time and growth rate of cells is crucial for:
- Cell Culture Studies: Understanding growth rates to optimize culture conditions and experiment timing.
- Microbial Research: Studying bacterial or yeast growth for applications in biotechnology, food safety, and disease control.
- Cancer Research: Analyzing tumor cell proliferation to assess growth patterns and treatment efficacy.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1: Calculate the growth rate and doubling time of a cell culture that grows from 10,400 cells/mL to 41,600 cells/mL in 24 hours:
- Initial Concentration: \( N_0 = 10,400 \, \text{cells/mL} \);
- Final Concentration: \( N_t = 41,600 \, \text{cells/mL} \);
- Duration: \( t = 24 \, \text{hr} \);
- Growth Rate Constant: \( k = \frac{\ln(41,600/10,400)}{24} = \frac{\ln(4)}{24} \approx 0.0578 \);
- Growth Rate: \( r = e^{0.0578} - 1 \approx 0.0595 \);
- Doubling Time: \( t_d = \frac{\ln(2)}{0.0578} \approx 12.0000 \, \text{hr} \);
- Result: \( r = 0.0595 \), \( t_d = 12.0000 \, \text{hr} \).
Example 2: Calculate the growth rate and doubling time of a bacterial culture that grows from 5,000 cells/L to 20,000 cells/L in 1,440 minutes, outputting doubling time in minutes:
- Initial Concentration: \( N_0 = 5,000 \, \text{cells/L} = 5 \, \text{cells/mL} \);
- Final Concentration: \( N_t = 20,000 \, \text{cells/L} = 20 \, \text{cells/mL} \);
- Duration: \( t = 1,440 \, \text{min} = 24 \, \text{hr} \);
- Growth Rate Constant: \( k = \frac{\ln(20/5)}{24} \approx 0.0578 \);
- Growth Rate: \( r = e^{0.0578} - 1 \approx 0.0595 \);
- Doubling Time: \( t_d = \frac{\ln(2)}{0.0578} \approx 12 \, \text{hr} = 720 \, \text{min} \);
- Result: \( r = 0.0595 \), \( t_d = 720.0000 \, \text{min} \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does the growth rate tell us about cell growth?
A: The growth rate (\( r \)) indicates the proportional increase in cell population per unit time, reflecting how quickly the population grows.
Q: Why might the doubling time vary between experiments?
A: Doubling time depends on factors like cell type, culture conditions (e.g., nutrient availability, temperature), and the presence of growth inhibitors.
Q: Can this calculator be used for bacterial cultures?
A: Yes, the formulas apply to any exponentially growing population, including bacteria, as long as the growth phase is exponential.
Cell Doubling Time Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back