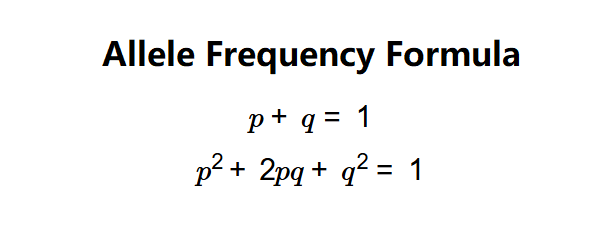1. What is the Allele Frequency Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the allele frequencies of normal (\( p \)) and mutant (\( q \)) alleles, as well as the genotype frequencies (\( p^2 \), \( 2pq \), \( q^2 \)), in a population under Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, based on the prevalence of a recessive disease.
Purpose: It is used in population genetics to estimate the likelihood of being a carrier of a recessive genetic disease, which is critical for understanding genetic diversity and disease risk in populations.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium equations:
- \( p + q = 1 \)
- \( p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1 \)
Where:
- \( p \): Frequency of the normal allele;
- \( q \): Frequency of the mutant allele;
- \( p^2 \): Frequency of homozygous dominant individuals (normal, \( AA \));
- \( 2pq \): Frequency of heterozygous individuals (carriers, \( Aa \));
- \( q^2 \): Frequency of homozygous recessive individuals (affected, \( aa \)).
Steps:
- Select the frequency type (proportion or percentage) for the recessive disease prevalence (\( q^2 \)).
- Enter the disease frequency (e.g., 1 in 10,000 or 0.01%).
- Calculate \( q \) as the square root of \( q^2 \).
- Calculate \( p \) as \( 1 - q \).
- Compute genotype frequencies: \( p^2 \), \( 2pq \), and \( q^2 \).
- Display all frequencies, formatted in scientific notation if the absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Allele Frequency Calculation
Calculating allele frequencies is crucial for:
- Genetic Counseling: Estimates the risk of passing on recessive genetic diseases to offspring, helping families make informed decisions.
- Population Genetics: Assesses genetic diversity and the prevalence of disease-causing alleles in a population.
- Public Health: Informs screening programs and preventive measures for genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis or sickle cell anemia.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1: Calculate the allele and genotype frequencies for a population where the recessive disease cystic fibrosis occurs in 1 in 2,500 individuals:
- Disease Frequency: 1 in 2,500;
- Homozygous Recessive Frequency: \( q^2 = \frac{1}{2500} = 0.0004 \);
- Mutant Allele Frequency: \( q = \sqrt{0.0004} = 0.02 \);
- Normal Allele Frequency: \( p = 1 - 0.02 = 0.98 \);
- Homozygous Dominant Frequency: \( p^2 = 0.98^2 = 0.9604 \);
- Heterozygous (Carrier) Frequency: \( 2pq = 2 \times 0.98 \times 0.02 = 0.0392 \);
- Result: \( p = 0.9800 \), \( q = 0.0200 \), \( p^2 = 0.9604 \), \( 2pq = 0.0392 \), \( q^2 = 0.0004 \).
Example 2: Calculate the allele and genotype frequencies for a population where a recessive disease occurs in 0.01% of individuals:
- Disease Frequency: 0.01%;
- Homozygous Recessive Frequency: \( q^2 = \frac{0.01}{100} = 0.0001 \);
- Mutant Allele Frequency: \( q = \sqrt{0.0001} = 0.01 \);
- Normal Allele Frequency: \( p = 1 - 0.01 = 0.99 \);
- Homozygous Dominant Frequency: \( p^2 = 0.99^2 = 0.9801 \);
- Heterozygous (Carrier) Frequency: \( 2pq = 2 \times 0.99 \times 0.01 = 0.0198 \);
- Result: \( p = 0.9900 \), \( q = 0.0100 \), \( p^2 = 0.9801 \), \( 2pq = 0.0198 \), \( q^2 = 0.0001 \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
A: Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium is a principle stating that allele and genotype frequencies in a population remain constant across generations in the absence of evolutionary forces like mutation, selection, or genetic drift.
Q: Why is the carrier frequency important?
A: The carrier frequency (\( 2pq \)) indicates the proportion of individuals who carry one copy of the mutant allele and can pass it to their offspring, which is critical for assessing disease risk in genetic counseling.
Q: Can this calculator be used for dominant diseases?
A: This calculator is designed for recessive diseases, where the disease frequency corresponds to \( q^2 \). For dominant diseases, a different approach would be needed to estimate allele frequencies.
Allele Frequency Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back